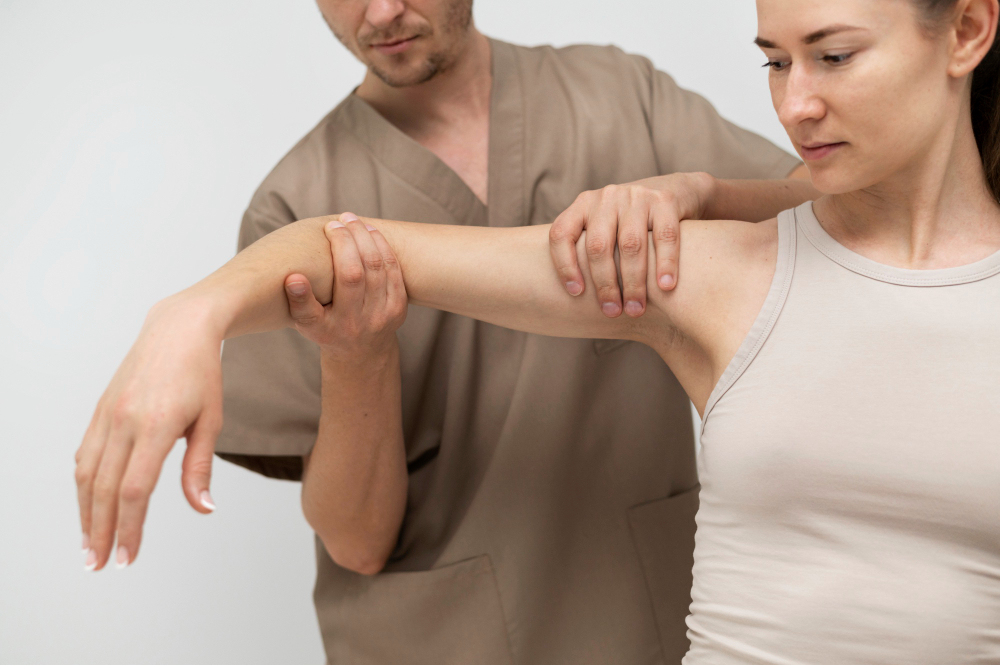
Nerve compression and muscle weakness are closely linked. Nerve compression happens when a nerve gets pressed or squeezed. This can cause pain, tingling, or numbness. Muscle weakness means your muscles do not work as well as they should. Often, nerve compression leads to muscle weakness. Understanding this connection helps you spot early signs and seek help. In this blog, we explain how nerve compression and muscle weakness are related. We also cover symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. If you want to know more about physiotherapy and rehabilitation, keep reading.
What Is Nerve Compression?
Nerve compression, also called a pinched nerve, happens when something presses on a nerve. This pressure can come from bones, muscles, or swelling. For example, a herniated disc in your back can press on a nerve. Sometimes, injuries or repetitive movements cause nerve compression. When nerves are squeezed, they cannot send signals well. As a result, you may feel pain or weakness. According to the CDC, nerve compression is a common cause of pain and numbness in adults.
How Does Nerve Compression Cause Muscle Weakness?
When a nerve is compressed, it cannot send messages to your muscles. Because of this, muscles may not get the signals they need to move. Over time, this leads to muscle weakness. For instance, if a nerve in your neck is pinched, your arm muscles may feel weak. In some cases, the weakness gets worse if the nerve stays compressed. Early treatment can help prevent lasting damage. Therefore, it is important to notice changes in your strength.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Nerve compression and muscle weakness often show clear signs. However, symptoms can vary based on which nerve is affected. Watch for these warning signs:
If you notice these symptoms, you should talk to a doctor. Early care can stop the problem from getting worse.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Identify the Link
Doctors use several steps to find out if nerve compression is causing muscle weakness. First, they ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they do a physical exam to check your strength and reflexes. Sometimes, doctors use tests like:
With these tests, doctors can find the exact spot of nerve compression. This helps them choose the best treatment for you.
Treatment Options and Rehabilitation Approaches
Treatment for nerve compression and muscle weakness depends on the cause. In many cases, doctors suggest simple steps first. For example, rest and gentle stretching can help. Other common treatments include:
Rehabilitation is important for recovery. Physiotherapists teach exercises to improve movement and prevent future problems. According to the WHO, early rehab can speed up healing and lower the risk of long-term weakness.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
Although not all cases can be prevented, you can lower your risk of nerve compression and muscle weakness. Try these tips:
By following these steps, you can protect your nerves and muscles. If you have any symptoms, seek help early.
In summary, nerve compression and muscle weakness are closely linked. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a big difference. Consult a physiotherapist or medical specialist for personalized advice.